What is CGNAT? Let's start by discussing Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
IPv4 is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol. It's responsible for establishing connections between devices based on their internet address. IPv4 was deployed in 1983, and at that time, no one could see the future growth of the Internet. And that growth isn't slowing down.
In 1983, IPv4 supported 4.3 billion addresses, which seemed enormous at the time. However, on November 25, 2019, the world ran out of IPv4 addresses, marking a critical turning point in the history of the internet.
IPv6
Thankfully, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) realized this problem and developed IPv6. This new Internet Protocol was supposed to solve the growing shortage of IP addresses by creating a replacement for IPv4.
Unfortunately, IPv6 isn't backward compatible with IPv4. And migrating to IPv6 is not just complex, but also a costly endeavor. Updating all servers, routers, and other equipment to IPv6 is overwhelming and expensive. As a result, migrating to IPv6 isn't practical for many broadband service providers, presenting a significant challenge.
Compounding this problem is the goal of governments and service worldwide to provide internet access for all. As a result, broadband providers are faced with the daunting task of continually buying additional IPv4 addresses to keep up with new subscribers being added, a financial burden that isn't sustainable in the long run.
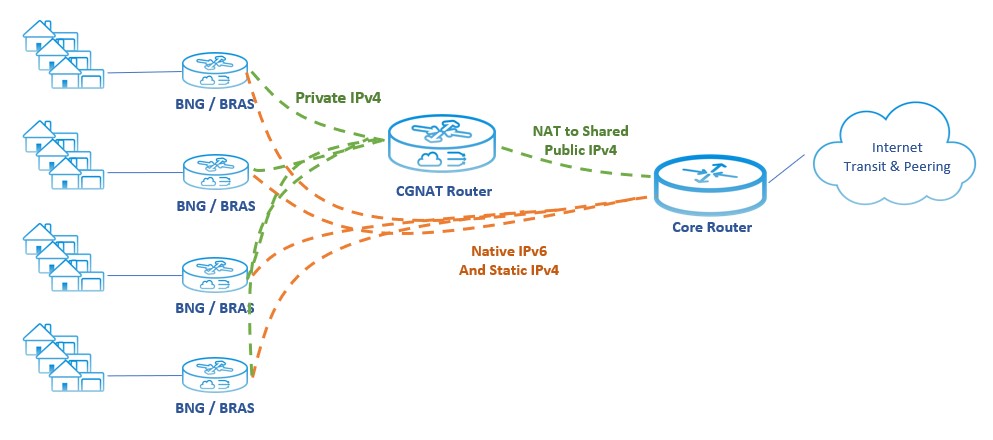
Carrier Grade NAT
Carrier-grade NAT (CGNAT) has become a popular solution. CGNAT enables multiple customers to share a single IP address. A CGNAT router acts as an agent between the Internet and a local private network (with many devices), so one public IP address can represent hundreds or thousands of private network devices.
CGNAT's technical name (NAT 444) refers to how the technology works: an end user receives a non-publicly routable IP address from the private series defined in RFC 1918. Before CGNAT, each internet user received a public IP address. With CGNAT, the broadband provider operates an intermediate network. This enables customer networks (with their own internal network address space) to route through the ISP's pool of public Internet IPv4 addresses for access to the Internet.
CGNAT limits an organization's use of public IP addresses by sharing one public IP address among many private IP addresses. This reduces the need to buy additional IPv4 addresses continually. As a result, CGNAT has become an essential solution to maximize the use of limited IPv4 addresses and successfully transition to IPv6.
Which CGNAT Solution is Best for My Network?
Many CGNAT solutions in the market have different features and price points. The key is to focus on the solution that's best for you. Large carriers may be interested in CGNAT solutions with the most advanced features. Regional and rural ISPs may be more interested in solutions that solve IPv4 exhaustion and are reasonably priced.
Stand-alone CGNAT solutions have traditionally run on proprietary hardware. Although these CGNAT systems may possess some advanced features, their proprietary nature (i.e., vendor lock-in) limits your choices and flexibility.
The Future Network is Software-Based and Disaggregated
The future of the network is software, and many broadband providers are turning to software-based CGNAT solutions. These solutions run on standard x86 servers. As a result, software-based solutions provide ISPs with more network flexibility and lower costs since there is no proprietary hardware to buy. The increased flexibility also enables providers to extend their IPv4 networks quickly.
CGNAT and Application Support
NAT translates IP addresses on the network layer (L3), which works well for most applications. However, it can cause problems for applications that include IP addresses on the application layer.
To make NAT work with these applications, address information in the application layer must be translated. To accomplish this, an application-level gateway (ALG) translates IP addresses in the payload of the application layer. This is critical to ensuring all applications work continuously. Therefore, ISPs should look for CGNAT solutions that support application layer gateways.
Performance
When subscribers access the Internet from one of their devices, they typically have no idea about the NAT activities that may be happening, nor do they care. To ensure IP address translation does not affect the customer experience, ISPs should evaluate CGNAT solutions for their performance and scalability. This should include supporting millions of NAT sessions and providing over 300 Gbps of bandwidth.
Costs
Broadband providers' biggest concern is the high costs of traditional CGNAT solutions. As mentioned earlier, most traditional CGNAT solutions run on proprietary hardware, and one commonality among proprietary solutions is high costs.
ISPs need to examine the costs of CGNAT solutions closely to reduce their prices. Hardware accounts for a large percentage of overall costs, so lowering the costs of CGNAT hardware will significantly impact the total cost of ownership (TCO).
An Alternative to High-Priced CGNAT
For broadband providers looking for a high-performance and cost-effective CGNAT, netElastic may be able to help. netElastic's software-based CGNAT is built on its high-performance virtual router technology, which is a very scalable software architecture. It delivers high translation performance while supporting various additional routing capabilities.
netElastic CGNAT also has built-in support for application gateways to ensure applications run continuously and transparently with CGNAT. Using DPDK and advanced packet processing, netElastic CGNAT can achieve near-line-rate throughput on 10G, 25G, 40G, and 100G interfaces. It's also highly scalable (scales by cores) and scales from 10 Gbps to 1 Tbps, delivering 3x the performance of similarly priced solutions. netElastic CGNAT also supports up to 12 million NAT sessions.
As the demand for internet access continues, so does the importance of CGNAT in conserving and prolonging the lifespan of IPv4 addresses. If you're looking for a powerful (yet economical) CGNAT to conserve IPv4 addresses, netElastic CGNAT delivers the lowest TCO in the industry.


